NEWS
A selection of FirstTouch's best football writing, brought to you by emerging journalists, collaborators, and fans.
Put aside the 93% of Spanish women following in the footsteps of the USWNT, protests over pay and working conditions are just starting
Discussions and debates about gender equality in football are all but just starting. A crescendo of the matter is surely at hand all around the world.
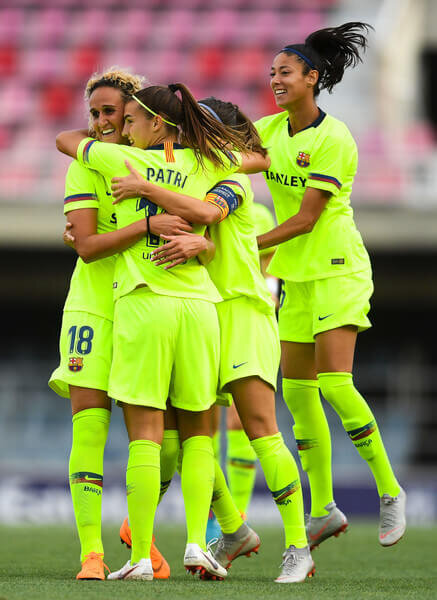
Patricia Guijarro of FC Barcelona celebrates with her team mates after scoring his team's first goal during the UEFA Women's Chamoions League round of 32 2nd leg between FC Barcelona Women and BIIK Kazygurt at the Mini Estadi on September 26, 2018 in Barcelona, Spain.
(Sept. 25, 2018 - Source: Getty Images Europe)
The unfortunate state of affairs
Players in Spain’s top-flight women’s league are in talks with the Association of Women's Soccer Clubs after a strike that saw eight games postponed on November 16th. The strike was in protest over the payment structure in the Primeira Division with players demanding a salary revision and better working conditions. Despite being one of the top women’s leagues in the world, players in the league feel that they are receiving the short end of the bargain from the authorities and after a year of failed negotiations, the players finally took decisive action on the matter. The protest is the first of its kind in Spain and an overwhelming 90% of the players from the 16 clubs represented in Primeira Division signed up to take part in the strike. The standoff came to an end after the Association of Women's Soccer Clubs moved to reopen negotiations.
The players have since reduced their demands to about €16,000 as the minimum wage from the initial €20,000. They are also asking for protection in the case that protects their maternity rights, working conditions and an increase in the minimum hours per week from 20 to 40 hours. One major challenge is that many of the players in the league are not considered full-time players and are only employed on a part-time basis which cuts their earnings drastically. This type of situation can be seen all over Europe for example in England, players in the Women’s Super League women earn an average of £18,000 whereas the male players in the English Premier League earn an average of £2.6 million a year leaving some to have to supplement their football careers with jobs to make ends meet. Spain is just the latest to experience the current wave sweeping across women’s football of players demanding fairer working conditions. Football is one of the most unequal sports and for the women playing in the game, their voices can now be heard loudly; “enough is enough, we want a fair system.”
USWNT: World Champions and women’s rights icons
The fight for better pay by women’s teams is all about fighting the system and demanding more equitable conditions and there is no better representation for this fight than the USWNT. Recently the world watched as the United States won the FIFA Women’s World Cup in France and immediately took the win as an opportunity to voice their issues in the press and sending a message to the world about the state of women’s football. Many would know of the ongoing dispute between the USWNT and the United States Soccer Federation over an unequal pay structure between the women’s and men's sides that has been playing out for a number of years. USA Women’s football team are champions and heroes off the field for their activism in the face of what they deem to be gender discrimination. In 2016, five players namely Carli Lloyd, Megan Rapinoe, Rebecca Sauerbrunn, Hope Solo and Alex Morgan also filed a wage discrimination complaint against their employers, the USA Soccer Federation. In March 2019, 28 players signed a class action lawsuit revealing details of perks and benefits that only the male team receive which included private jets and winning bonuses that were substantially higher for the US Men’s team. A big argument for the USWNT is that their record is far more impressive with more games and trophies won that the male team but receive substantially lower salaries and benefits.
“To create a snapshot of the odds against female footballers we can take a look at the fact that Lionel Messi earns more in salaries that the professional women players in the top seven leagues combined.”
The example that USWNT has set in deciding to battle it out with their employers has undoubtedly caused the issue to be brought to the forefront and has had a cascading impact on the rest of women’s football. Their decision to take the fight to the public has seemingly inspired other players to do the same. Players speaking out on this issue, are actually starting to make a difference. For example, Norway's women’s football team won equal pay in 2017 after the men’s team forfeited some of their benefits. In other cases, the associations and the players settle their disputes outside of court and in private as in the case of the Australian national team which reached a deal where they would be awarded the same pay as the men’s team. The Matildas will also be allowed to travel business class for international travel and a commitment from the national governing body to raise coaching standards. Fighting this battle on the public domain has its benefits and most importantly that fans can see it all play out as is the case of USWNT. Fans have since backed and supported the team in their quest for equal pay chanting, “equal pay” as the players went up to receive their medals during the FIFA World Cup final. USWNT fearless approach in demanding fair compensation has galvanized support for the cause and a growing movement around equal pay in the United States and in the worldwide media. Although the USWNT case was under mediation, the talks stopped after what the federation was unwilling to meet the demands set by the players. Megan Rapinoe the co-captain and most vocal player said, “When [US Soccer] is ready to have a serious conversation about equal pay, I think the conversations will go better."
Megan Rapinoe of the USA celebrates after scoring her team's first goal during the 2019 FIFA Women's World Cup France Final match between The United States of America and The Netherlands at Stade de Lyon on July 07, 2019 in Lyon, France.
(July 6, 2019 - Source: 5021154/Getty Images Europe)
Steps being taken by players around the world
In Italy, the Women’s team is still considered amateurs according to law and therefore they are currently allowed to earn up to €33,000 before taxes because of the amateur status a law that is archaic. Football in Italy is not traditionally a woman’s sport and as such there are many barriers for women. Despite this, the Italian women’s team qualified for their first World Cup in 20 years and made it to the quarter-finals. The momentum from their World Cup performance has led to more Italians backing the women’s team. The conditions in Italy still represent a culture that views football as a male sport, however, the perceptions in the country are beginning to shift due to the performance of the women’s team to qualify for the World Cup, whereas the Azzurri failed to qualify for the men’s edition in 2018.
One player who has been vocal about the issue in Italy and who is behind the movement to usher in Italian football into the modern era is Juventus player Barbara Bonansea. She believes that the increase in viewership should correspond with the remuneration for female players; “If there’s more coverage of our games and more sponsors come in, then we deserve more, too.” It is common that the women’s teams which in most cases have better records than the men’s teams do not get rewarded in an equitable manner for their exploits on the field. Taking the issue to the African continent, Africa’s most successful women’s team, Super Falcons have also been vocal in the conversation around unequal payment systems. While participating in tournaments, the men's team receives $10,000 for a win and $5,000 for a draw while the Super Falcons can expect $3,000 and $1,500. The Super Falcons have demonstrated in protest of unpaid allowances. Forward, Desire Oparanozie called for equal pay noting that the teams were just as successful as the men’s; "We are the most successful female team in Africa, yet we have the largest disparities between men's and women's pay," Super Falcons have won 11 AFCON titles and the last three competitions. Progress is being made elsewhere in Nigeria, in Edo State, where the women and men’s teams are going to be paid the same after the authorities saw that paying women less was more of a gender issue than a performance issue. It’s a small win for women’s football in Nigeria and with time, this trend will catch on to the rest of the continent.
Jackie Groenen of the Netherlands kisses the trophy following the Final of the UEFA Women's Euro 2017 between Netherlands v Denmark at FC Twente Stadium on August 6, 2017 in Enschede, Netherlands.
(Aug. 5, 2017 - Source: Maja Hitij/Getty Images Europe)
What will it really take to achieve equality?
To create a snapshot of the odds against female footballers we can take a look at the fact that Lionel Messi earns more in salaries that the professional women players in the top seven leagues combined. The gap is saddening and reveals a desperate need for change. This is possibly the start of a push back from players on the working conditions and it’s good and welcome progress the sport. As Megan Rapinoe puts it, a paradigm shift and a completely new way of looking at women’s football is necessary if the change is ever to come to the game. Equal pay might still be an ideal today but through the continued work of women in the sport, it could soon be a reality. To achieve equality, we are talking about having to look beyond just beyond revenues that women earn and start making headway on trying to invest in teams and marketing of the sport. The women’s game is a long way to go in terms of receiving as much investment and attention it needs.
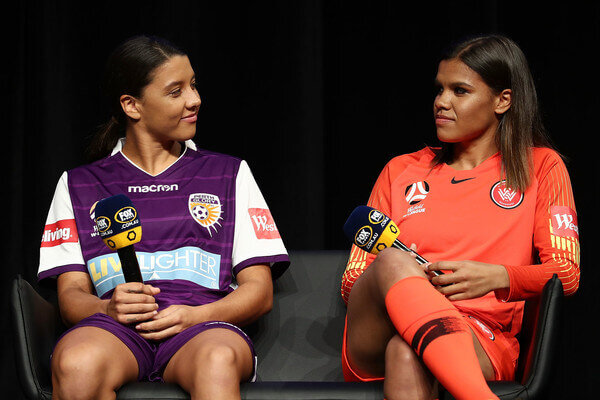
Jada Whyman of Western Sydney Wanderers FC and Sam Kerr of Perth Glory speak on stage during the 2018/19 A-League Season Launch at Fox Studios on October 15, 2018 in Sydney, Australia.
(Oct. 14, 2018 - Source: Mark Metcalfe/Getty Images AsiaPac)
It’s a system-wide problem, even at the FIFA Women’s World Cup the players received less amount for an appearance fee and the tournament prize is only a fraction of the prize money awarded at the FIFA Men’s World Cup. The prize money for the 2019 FIFA World Cup was $30 million, twice the amount paid in the previous tournament. In 2018 FIFA prizes for the Men’s tournament went up to $400 million, a difference of more than ten times. FIFA has promised to invest half a billion dollars in Women’s game over the next few years. Progress is being made. For example, it increased the number of teams for the world cup to 32 from 24 as a way to boost women’s football and create space for talent. Although FIFA is not in charge of how prize money is distributed in each of the federations, there is room for regulations that allow female players to receive their fair share from the National federations.
Final thoughts
Currently, the male game is more popular and receives resoundingly more attention than the female game. Women’s football is more popular than it has ever been and as such, it is the appropriate time to iron out the issues in the game. Some countries that have reached positive agreements after giving equal pay at the national team level including New Zealand, the Netherlands proving that it is not so difficult to reach an equitable decision. These players are simply asking to be able to play the game as professionals just like in the men. It’s yet to be seen what will come out of the negotiations between the players and the authorities in Spain. The hope is that this strike can be added to the list of wins in women’s football.
To what extent are local football associations determining results by successive pay-dispute rows?
Zimbabwe, Nigeria, Cameroon, only to mention but a few, are some of the sides that have had their overall performances negatively impacted by off the pitch scandals of late or non-payment resulting from maladministration and corruption. What’s local football associations’ role in this? How far does the cancer go? Simiso answers it all.
Introduction
Local football associations are the seedbeds for continental talent. Before we meet players at large tournaments like the Africa Cup of Nations and FIFA World Cup, the conditions that they are subjected to while within their localities actually determine their overall performance. Over the years, several teams have had pay disputes with their national associations. They have refused to board planes and have even threatened to boycott some matches without getting their pay. This article wants to dig deeper into this problem by analysing some of the underlying issues and what the implications of pay disputes are on African football. Before that, we will take a quick look at some countries that have fallen victim to this problem.
“By the time a whole team has agreed to boycott a game, it means the individual frustration that comes with being unpaid has mounted to a team level. Imagine how a group of frustrated players are supposed to train together, take each other’s mistakes and say their chants with high voices and joy. It is almost impossible.”
Cameroon supporters cheer for their team ahead of the 2017 Africa Cup of Nations group A football match between Cameroon and Guinea-Bissau at the Stade de l'Amitie Sino-Gabonaise in Libreville on January 18, 2017. / AFP / GABRIEL BOUYS
(Jan. 17, 2017 - Source: AFP)
Cameroon
Cameroon came 24 hours after the deadline because the Cameroonian Football Federation had delayed to pay their salaries and bonuses. This is in spite of the fact that the tournament regulation stipulates that teams should arrive at the host country at least 5 days before their opening game. In light of that, Cameroon might have to pay a fine for that. Is that irresponsibility? Definitely, not. The team refused to board a plane to Egypt because they demanded their salaries to be doubled for playing in the tournament. This was one of the players’ last technic. They had agreed to only 25% on their salaries and bonuses and even paid for their plane tickets to training camps which were held in Madrid and Doha. Such sacrifices are a testament of how much the players are willing to do for their country if only that would be complemented by efforts from the government.
Nigeria
Nigeria almost missed their 2013 FIFA Confederation Cup campaign after they also refused to fly out of Nigeria without their bonuses being paid. The most daring one and my personal favourite was that of the Super Falcons who decided to stay in their hotels in France and not fly out unless their bonuses are paid. In 2016, they also protested after they won the African Women’s Cup of Nations. It is very hard to understand how a team that has demonstrated consistent excellence is not paid on time. There are countries that would kill to have teams that play like the Nigerian Women’s national team.
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe national team did go on the plane but refused to go for training while they were in Egypt as a way to express their grievances against the Zimbabwe Football Federation. They too had not been paid for some time. They also threatened to miss their first game if their accounts were not credited on time. Despite having a talented squad that looked quite promising, the Warriors were eventually eliminated from the group stages.
Where is the problem?
Guinea-Bissau's forward Piqueti advances with the ball past Cameroon's defender Collins Fai before scoring a goal during the 2017 Africa Cup of Nations group A football match between Cameroon and Guinea-Bissau at the Stade de l'Amitie Sino-Gabonaise in Libreville on January 18, 2017. / AFP / GABRIEL BOUYS
(Jan. 17, 2017 - Source: AFP)
For countries like Nigeria whose players have continuously done this to prove that this is not a one-time off problem but a challenge that is deeply engraved in the system, problems such as corruption and mismanagement of funds have been cited as some of the major causes for these pay disputes. Even when the money leaves the government coffers intended for the soccer players, for some reason it finds itself in the pockets of government officials who have perhaps not kicked a ball in decades. Corruption is such a rampant problem that has stifled many sectors of African governments. The bigger problem is that some African countries do not generally prioritise sports so much they are not given adequate funding. Private companies come in to sponsor local soccer leagues with the hope that the government will come in to take care of the national team. For example, in South Africa there is the ABSA Premiership and the MTN Super 8 which are sponsored by private companies. Instead, the government will give excuses about more pressing problems that need to be taken care of in the country. What makes things even worse is that some federations would not proactively communicate their challenges ahead of time. Sometimes, well-communicated disappointment is better than unkept promises. Some governments will go all the way to signing contracts with players only to go silent on them when it is time to pay. For example, Cameroon had a presidential decree in 2014 that stipulated that all salaries and bonuses will be paid at the commencement of any tournament. Was it ever upheld though? We told that story already.
Asisat Oshoala of Nigeria reacts after missing a breakaway attempt during the FIFA Women's U-20 Final against Germany at Olympic Stadium on August 24, 2014 in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Photo by Richard Wolowicz/Getty Images)
(Aug. 23, 2014 - Source: Richard Wolowicz/Getty Images North America)
Setting a precedent
Under no circumstances is it ever justifiable for anybody to work with no compensation, but why is it important for governments to set the right precedent for national teams? Firstly, the amount of effort it takes to get into the national team just deserves the rightful amount of compensation. Most of the players that make it to the national teams are their local teams’ star players and some have become so good that they have been outsourced by teams outside of their countries. The saturation of unquestionable talent in most national teams across Africa should prompt governments to do the right thing.
Sports has become the escape route from social ills for most African youths. In a continent with high unemployment rates and pressure to engage in crime and corruption, sports is the unifying factor for young people that helps them evade these things. Beyond the fitness benefits that soccer comes with, it is also a sport that requires dedication, discipline and focus. Playing at the highest level of this taxing soccer journey should be rewarded profusely so that other young people can be motivated to continue working hard. If you cannot give African youth jobs, then at least give them the motivation to work hard on something.
Impact on performances
We have already established that the ability to win a game is not just determined by the talent and skills displayed on the field. It is also determined by the players’ emotional and mental wellbeing. Compensation gives one the motivation and aspiration to do more. In the absence of that, the opposite can also be true. It is not a shock that Cameroon went into AFCON 2019 as champions but barely made it far in the tournament. They were eliminated by Nigeria at the round-of-16 stage.
Team Germany poses for a photo with the championship trophy and their gold medals during the FIFA Women's U-20 Final at Olympic Stadium on August 24, 2014 in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Germany defeated Nigeria 1-0 in overtime.
(Aug. 23, 2014 - Source: Richard Wolowicz/Getty Images North America)
It also destroys team morale. By the time a whole team has agreed to boycott a game, it means the individual frustration that comes with being unpaid has mounted to a team level. Imagine how a group of frustrated players are supposed to train together, take each other’s mistakes and say their chants with high voices and joy. It is almost impossible. There is only so much that a good coach can do for them when they are not intrinsically motivated.
Conclusion
Before we blame players for not being focused or not training hard enough, it is important that we look at issues such as pay disputes that affect how much they can bring to the field. It has also transpired that the problem is with internal systems that do not prioritise or facilitate the timely payment for the players. Sadly, national teams which are meant to be countries’ pride are then not able to perform to their best levels due to factors that could be avoided. The lack of transparency also does not make it any better.
With all that said, do you think teams are actually justified in boycotting matches and tournaments in order to get the attention of their governments?